My Garage
My Account
Cart
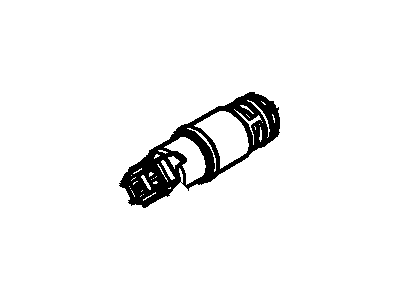
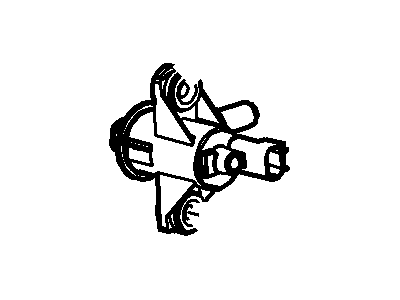
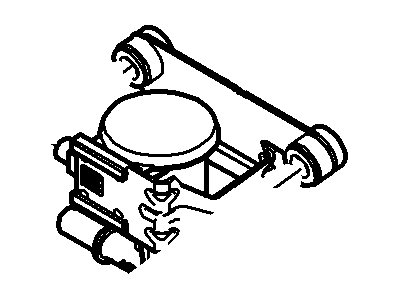
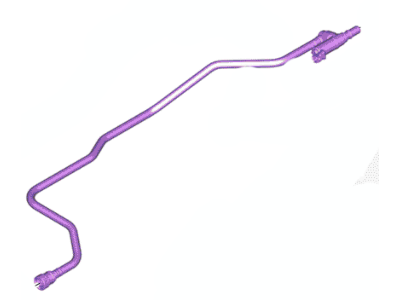
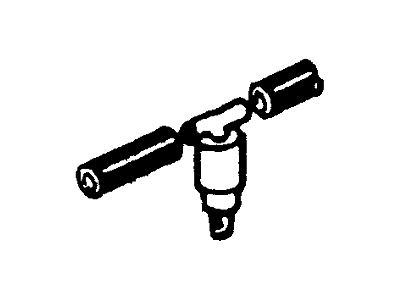
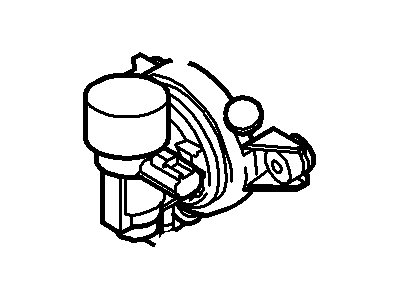
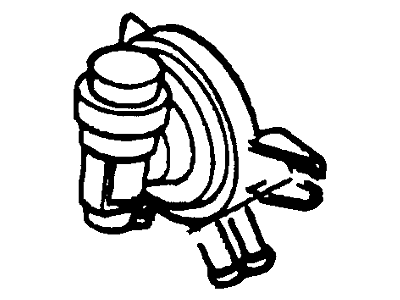
Genuine Ford F-150 Canister Purge Valve
Vapor Canister Purge Valve EVAP- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
32 Canister Purge Valves found
Ford F-150 Solenoid Assembly
Part Number: 9U5Z-9F945-F$86.64 MSRP: $126.67You Save: $40.03 (32%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Valve Assembly
Part Number: 9U5Z-9C915-BE$57.42 MSRP: $94.91You Save: $37.49 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Purge Valve
Part Number: 6L3Z-9C915-A$102.96 MSRP: $170.18You Save: $67.22 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Valve Assembly
Part Number: 7L3Z-9C915-A$96.91 MSRP: $163.45You Save: $66.54 (41%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Valve Assembly
Part Number: 5L3Z-9C915-AA$102.96 MSRP: $170.18You Save: $67.22 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Vent Control Solenoid
Part Number: 9U5Z-9F945-C$45.60 MSRP: $72.73You Save: $27.13 (38%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord F-150 Valve Assembly
Part Number: JL3Z-9D333-D$285.89 MSRP: $460.00You Save: $174.11 (38%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysFord F-150 Valve Assembly - Fuel Vapour
Part Number: E7DZ-9B593-A$21.36 MSRP: $33.20You Save: $11.84 (36%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Solenoid Assembly
Part Number: 6L3Z-9F945-A$122.10 MSRP: $185.00You Save: $62.90 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Vapor Canister Purge Solenoid
Part Number: 4U5Z-9J451-DA$48.14 MSRP: $79.00You Save: $30.86 (40%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysFord F-150 Fuel Vapor Solenoid Power Train Canister Vent Valve
Part Number: F75Z-9F945-CA$102.94 MSRP: $150.50You Save: $47.56 (32%)Ford F-150 Valve Assembly
Part Number: JL3Z-9D333-C$233.91 MSRP: $376.36You Save: $142.45 (38%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Solenoid Assembly
Part Number: F7DZ-9F945-AA$88.12 MSRP: $128.83You Save: $40.71 (32%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord F-150 Fuel Tube Support Bracket
Part Number: L1MZ-9B325-A$101.40 MSRP: $153.63You Save: $52.23 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 32 Results
Ford F-150 Canister Purge Valve
We provide a wide range of Ford F-150 Canister Purge Valve at the best prices possible. If you need Ford F-150 Canister Purge Valve, you can shop with confidence on our website. All our OEM parts come with a manufacturer's warranty and are delivered to your door step with a fast delivery service.
Ford F-150 Canister Purge Valve Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What Are the Functions and Component Replacement Procedures for the Evaporative Emissions Control System,Canister Purge Valve and Vapor Canister on Ford F-150?A:EVAP stands for Evaporative Emission Control and EVAP system is responsible for succumbing the fuel vapors and then emitting it into the intake manifold once the car engine is running so as to mix with the arriving air fuel mixture. The various parts of the EVAP system are the EVAP canister, the vent solenoid, the filter tube, the dust separator and the canister purge valve, with the canister together with related components situated within the vehicle above the spare tire while the purge valve is situated in the engine compartment adjacent to the brake fluid reservoir. Other accessories include Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP) sensor, Fuel Limit Vent Valve (FLW) assembly, check valve for fuel filler pipe, cap for filler neck as well as the EVAP system check. Overfilling and vapor escape is eliminated by the use of fuel filler neck cap and the FLW assembly has the responsibility of controlling the flow of fuel vapor and prohibiting the entry of liquid fuel into the EVAP lines in a case of a vehicle rollover. The FTP sensor triggers the purge valve where tank pressure is high, it also measures vacuum levels during testing. The EVAP system monitor in a vehicle will perform a 'running loss system leak test' in which the engine is started and tested for large leaks, before running the test to note the rate of decay as an indicator of minor leaks. For component replacement, there are the EVAP canister purge valve which at the removal, entails disconnecting the electrical connector and quick-connect couplings as well as releasing it from the mounting bracket. The EVAP canister assembly comprised different parts, and to check or replace any component, the negative terminal of the battery has to be disconnected, car has to be raised and some hoses and mounting bolts have to be disconnected or removed, and after installation, all the parts are refitted in the reverse order.
Related Ford F-150 Parts
Browse by Year
2023 Canister Purge Valve 2022 Canister Purge Valve 2021 Canister Purge Valve 2020 Canister Purge Valve 2019 Canister Purge Valve 2018 Canister Purge Valve 2017 Canister Purge Valve 2016 Canister Purge Valve 2015 Canister Purge Valve 2014 Canister Purge Valve 2013 Canister Purge Valve 2012 Canister Purge Valve 2011 Canister Purge Valve 2010 Canister Purge Valve 2009 Canister Purge Valve 2008 Canister Purge Valve 2007 Canister Purge Valve 2006 Canister Purge Valve 2005 Canister Purge Valve 2004 Canister Purge Valve 2003 Canister Purge Valve 2002 Canister Purge Valve 2001 Canister Purge Valve 2000 Canister Purge Valve 1999 Canister Purge Valve 1998 Canister Purge Valve 1997 Canister Purge Valve 1996 Canister Purge Valve 1995 Canister Purge Valve 1994 Canister Purge Valve 1993 Canister Purge Valve 1992 Canister Purge Valve 1991 Canister Purge Valve 1990 Canister Purge Valve 1989 Canister Purge Valve 1988 Canister Purge Valve 1987 Canister Purge Valve 1986 Canister Purge Valve 1985 Canister Purge Valve 1984 Canister Purge Valve 1983 Canister Purge Valve 1982 Canister Purge Valve 1981 Canister Purge Valve 1980 Canister Purge Valve