My Garage
My Account
Cart
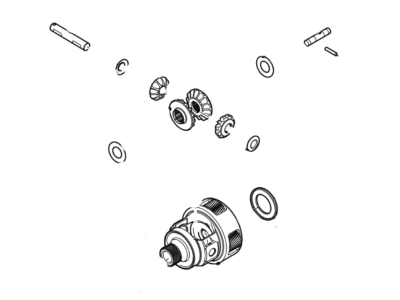
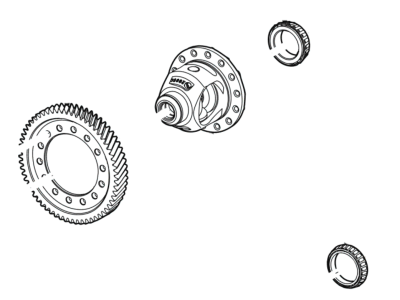
Genuine Ford Taurus Differential
Front Differential- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
5 Differentials found
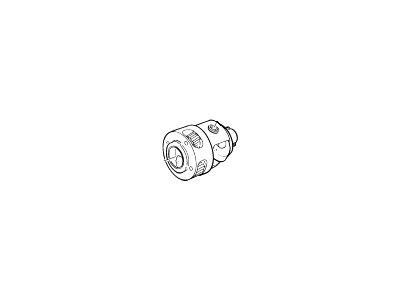
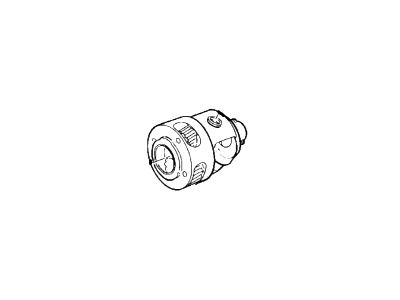
Ford Taurus Planet Gear Assembly
Part Number: 9L8Z-7F465-H$237.30 MSRP: $350.00You Save: $112.70 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysFord Taurus Planet Gear Assembly
Part Number: 8A8Z-7F465-P$433.81 MSRP: $639.83You Save: $206.02 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Ford Taurus Differential
The Ford Taurus has what is known as a differential, this is an important part of the car's drive train and is used to divide the power that is received from the engine to the wheels. This mechanism is important in enabling the wheels to rotate at different speeds especially during turning and this is very vital. The differential of the Ford Taurus helps to control the amount of power transfer to the wheels while at the same time help in controlling the torque and preventing strain on the drivetrain. For the past years, Ford Taurus has had different types of differentials that are used to meet certain driving requirements and conditions. Some of the types of differentials are; Open differentials; Limited-slip differentials (LSD). The open differential on the other hand, helps the power to be divided equally to the wheels, which is necessary in normal driving conditions. On the other hand, the LSD is better used in tough circumstances since it divides the power between the wheels depending on which has the most grip and this makes the handling of the Ford Taurus better on icy roads. All the three types of differentials have their own strengths and weaknesses, which define ways in which the Ford Taurus will handle in different conditions. For instance, the open differential may be a problem in the Ford Taurus when driving in slippery roads because the torque is divided equally between the two wheels; the LSD, on the other hand, has improved traction control and is therefore a better option for the Ford Taurus in such conditions.
We provide a wide range of Ford Taurus Differential at the best prices possible. If you need Ford Taurus Differential, you can shop with confidence on our website. All our OEM parts come with a manufacturer's warranty and are delivered to your door step with a fast delivery service.
Ford Taurus Differential Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to remove the differential with an Active Torque Control Coupling (ATCC) on Ford Taurus?A:On AWD models, an Active Torque Control Coupling (ATCC) manages power distribution to the front and rear wheels, typically directing most torque to the front. When wheel slip is detected, the ATCC system automatically increases torque to the rear wheels, continuously monitoring conditions and adjusting torque via an electric clutch in the rear axle. The ATCC operates without a mode selector or driver input, and the solenoid is non-repairable, requiring replacement of the entire rear axle assembly. To begin, raise the rear of the vehicle and support it securely on jackstands, blocking the front wheels to prevent rolling. Remove the driveshaft and driveaxles, then remove the rear stabilizer bar, which on Five Hundred and Montego models only needs to be slid forward for clearance. Support the differential with a floor jack and disconnect any electrical connectors. For 2007 and earlier models, remove the differential cross-bracket bolts and bracket, the front insulator bolt, and the two rear insulator bolts, noting that the passenger rear insulator bolt cannot be removed until the differential is taken out. For 2008 and later models, remove the four bolts securing the front of the differential to the front brackets, loosen the front mounting brackets from the subframe, and swing them out for clearance. Then, remove the six bolts securing the differential to the rear mounting brackets, lower the differential slightly, and disconnect any remaining connectors. Finally, lower the differential with the floor jack and install by reversing the removal steps, ensuring all fasteners are tightened to the specified torque.
Related Ford Taurus Parts
Browse by Year
2019 Differential 2018 Differential 2017 Differential 2016 Differential 2015 Differential 2014 Differential 2013 Differential 2011 Differential 2007 Differential 2006 Differential 2005 Differential 2004 Differential 2003 Differential 2002 Differential 2001 Differential 2000 Differential 1999 Differential 1998 Differential 1997 Differential 1996 Differential 1995 Differential 1994 Differential 1993 Differential 1992 Differential 1991 Differential 1990 Differential 1989 Differential 1988 Differential 1987 Differential 1986 Differential