My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Ford Explorer Shock Absorber
Suspension Shock Absorber- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
129 Shock Absorbers found
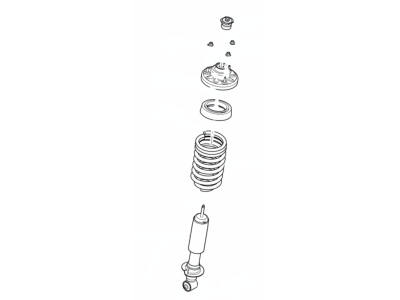
Ford Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-J$135.30 MSRP: $223.64You Save: $88.34 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-V$135.30 MSRP: $223.64You Save: $88.34 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: DB5Z-18125-H$85.58 MSRP: $141.45You Save: $55.87 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Kit
Part Number: 5U2Z-18V124-MA$51.73 MSRP: $87.09You Save: $35.36 (41%)Ford Explorer Front Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: EB5Z-18124-A$105.84 MSRP: $147.03You Save: $41.19 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: DB5Z-18124-AC$128.37 MSRP: $217.11You Save: $88.74 (41%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Front Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: DB5Z-18124-AE$126.68 MSRP: $209.38You Save: $82.70 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: DB5Z-18125-G$85.27 MSRP: $143.82You Save: $58.55 (41%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-M$135.30 MSRP: $223.64You Save: $88.34 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Front Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-W$139.70 MSRP: $230.91You Save: $91.21 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-S$169.40 MSRP: $280.00You Save: $110.60 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-T$135.30 MSRP: $223.64You Save: $88.34 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-P$116.42 MSRP: $196.36You Save: $79.94 (41%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Front Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: FB5Z-18124-U$139.70 MSRP: $230.91You Save: $91.21 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: F5TZ-18124-B$51.73 MSRP: $87.09You Save: $35.36 (41%)Ford Explorer Strut Loaded Assembly
Part Number: GU2Z-18A092-C$158.30 MSRP: $216.29You Save: $57.99 (27%)Ford Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: XL2Z-18124-BA$51.73 MSRP: $87.09You Save: $35.36 (41%)Ford Explorer Shock Absorber Assembly
Part Number: DB5Z-18125-A$85.58 MSRP: $141.45You Save: $55.87 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Explorer Shock Absorber Kit
Part Number: 5U2Z-18V125-T$95.61 MSRP: $130.64You Save: $35.03 (27%)
| Page 1 of 7 |Next >
1-20 of 129 Results
Ford Explorer Shock Absorber
The Shock Absorber in Ford Explorer vehicles is very vital in improving the comfort of the car through shocks and vibrations absorbed by the part. This mechanical device translates the energy being produced into heat and then dispersing the heat thus lessening the effect of harsh terrains. Contemplating the Ford Explorer car model, it is possible to distinguish types of the shock absorbers and they are distinguished between twin tube and mono tube kinds. Twin-tube shocks are prevalent and can be gas charged for longer life while mono-tube shocks are optimal suited for heat transfer and performance for the shocks enabling the cross direction installation. For the years, innovations in the shock absorber designs have brought with them elements such as Position Sensitive Damping (PSD) and Acceleration Sensitive Damping (ASD) that enables specific responses based on driving style. Also, semi-active systems which include Electrorheological (ER) and Magnetorheological (MR) dampers help in offering dynamic comfort and control. In general, the Shock Absorber is very crucial in allowing the Ford Explorer to perform as expected and support its ride quality.
We provide a wide range of Ford Explorer Shock Absorber at the best prices possible. If you need Ford Explorer Shock Absorber, you can shop with confidence on our website. All our OEM parts come with a manufacturer's warranty and are delivered to your door step with a fast delivery service.
Ford Explorer Shock Absorber Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to check CV Boot and Shock Absorber on Ford Explorer?A:The steering linkage and the suspension parts should also be inspected after certain periods as damaged or rusty parts usually cause odd wearage of tires, poor comfort of the ride and low fuel efficiency. To inspect the shock absorbers one ought to park the car on a level surface, switch off the engine, apply the handbrake. Ensure the tyres are well inflated and then compress a corner of the car and release and it should not rebound more than once or twice. If it's still in motion and does not assume its natural position or if it remains so, it may be so worn out that it requires replacement of its shock absorber. Perform this check on all corners and then lift the vehicle on jack stands with the air suspension switch off if equipped with the Automatic Ride Control. Check the fluids on the shock absorbers stating that any noted on them is from the shocks. Look for proper installation, and security as well as signs of abuse, if any, replace them in pairs. When it comes to the behavioral checks of the steering and suspension, look out for signs of damage, leakage or distortion of the components. Wipe the steering knuckle and have a partner articulate the tyre by wiggling the tyre to check at the ball joints; once the ball joints move, then they need replacement. Pick one of front tires and take hold in front tires and check the play in the steering linkage tight the mounts if necessary, check the ball joints for wear and tear. For front, refer to play or noise for wheel bearings, louder and more obvious on the 95 and later 4wd models which contain sealed hubs. Finally, examine the drive axle boots in 2001 and later 4WD vehicles for tears, cracks or even loose clamps and to check for leaks try to flex it; any single damage among them requires the checking of joints or boots.
Related Ford Explorer Parts
Browse by Year
2023 Shock Absorber 2022 Shock Absorber 2021 Shock Absorber 2020 Shock Absorber 2019 Shock Absorber 2018 Shock Absorber 2017 Shock Absorber 2016 Shock Absorber 2015 Shock Absorber 2014 Shock Absorber 2013 Shock Absorber 2012 Shock Absorber 2011 Shock Absorber 2010 Shock Absorber 2009 Shock Absorber 2008 Shock Absorber 2007 Shock Absorber 2006 Shock Absorber 2005 Shock Absorber 2004 Shock Absorber 2003 Shock Absorber 2002 Shock Absorber 2001 Shock Absorber 2000 Shock Absorber 1999 Shock Absorber 1998 Shock Absorber 1997 Shock Absorber 1996 Shock Absorber 1995 Shock Absorber 1994 Shock Absorber 1993 Shock Absorber 1992 Shock Absorber 1991 Shock Absorber