×
- Live Chat
- 1-888-788-9341


My Garage
My Account
Cart
This part fits
2013 Ford Taurus (VIN: 1FAHP2KT5DG183206) 6 Cyl 3.5L DOHC T/C; 6-Speed Automatic Transmission 6F55; Four-Wheel Drive (Full Time) (Left Hand Drive); SHO
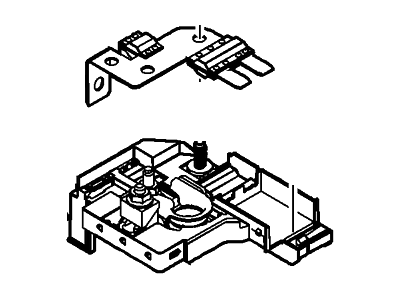
Check another vehicleFord DA8Z-14526-A Circuit Breaker Assembly
2011-2019 Ford DA8Z14526A
Customer Questions & Expert Answers (3)
- Part DescriptionCircuit Breaker Assembly
- B+ Stud Cover , Fuse Box , Includes Battery Positive Terminal Assy , Includes Megafuse
- Base No.14526
- Replaces
- ManufacturerFord
This part fits
2013 Ford Taurus (VIN: 1FAHP2KT5DG183206) 6 Cyl 3.5L DOHC T/C; 6-Speed Automatic Transmission 6F55; Four-Wheel Drive (Full Time) (Left Hand Drive); SHO
Check another vehicle$58.52 MSRP: $96.73 1
You Save: $38.21 (40%)
Ships in 1 Business Day
- Related Parts
- Product Specifications
- Customer Questions & Expert Answers
Product Specifications
Brand Genuine Ford Base No. 14526 Manufacturer Part Number DA8Z-14526-A, DA8Z14526A Part Description Circuit Breaker Assembly Other Names Circuit Breaker Item Dimensions 6.2 x 6.0 x 4.5 inches Item Weight 1.10 Pounds Condition New Fitment Type Direct Replacement Replaces BB5Z-14526-AA Manufacturer Ford SKU DA8Z-14526-A Warranty This genuine Ford part is guaranteed by Ford's factory warranty. Shipping & Return Shipping Policy Return Policy Warning: California's Proposition 65Customer Questions & Expert Answers
- Q:I am wondering if this is the exact part that fits in Posted by FordPartsGiant Specialist
- A:You can Select Your Vehicle to check if DA8Z-14526-A fits your vehicle.Posted by FordPartsGiant Specialist
- Q:What are fuses and how do they protect electrical circuits on Ford Taurus? Posted by Customer
- A:The electrical circuits of the vehicle are safeguarded by a combination of fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links, with the main fuse/relay panel located in the engine compartment and the interior fuse/relay panel found inside the passenger compartment. Fuses come in small, medium, and large sizes, all featuring the same blade terminal design, where medium and large fuses can be removed by hand, while small fuses require pliers or a plastic fuse-puller tool. Fusible links are situated in the harness to the right of the underhood fuse box and protect circuits that are not typically fused or that carry high current, such as the connection between the alternator and the battery. When an electrical component fails, checking the fuses is essential, using a test light to verify power at the terminal tips; if power is present on one side but absent on the other, the fuse is blown, which can also be visually confirmed by inspecting the element between the terminals. It is crucial to replace blown fuses with the correct type, as using fuses of different ratings, even if they fit physically, is not advisable since each circuit requires specific protection. If a replacement fuse fails immediately, the underlying issue, often a short circuit due to damaged wiring, should be addressed before installing another fuse. When replacing a blown fusible link, it is important to use one of the same specification, and if it blows again, troubleshooting the circuit is necessary before installing a new link.Posted by FordPartsGiant Specialist
- Q:Does the circuit breaker come with the red cover? Posted by Customer
- A:Yes, the red cover is includedPosted by FordPartsGiant Specialist 15/9/2020
If you have any questions about this product, please don't hesitate to ask us. We will be happy to help you!- Q:
Why choose Ford Parts Giant
- Dedicated Service
Your complete satisfaction is our #1 goal
- Lowest Prices
Best deals on genuine OE parts from dealerships
- Fast Delivery
Orders are processed and delivered promptly